What is Cervical Cancer?
Cancer is a disease that occurs when cells grow abnormally. When cancer begins in the cervix, it is called cervical cancer. Cervical cancer is caused by cell changes caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus can move from one individual to another by contact during sex. However, cervical cancer itself cannot be contagious to other individuals.
Cervical Function
1) Generates moisture to lubricate the vagina
2) Produces mucus to help sperm movement
3) Accommodates the baby in the womb during pregnancy
4) Allow menstrual blood to flow from the uterus to the vagina
Types of Cervical Cancer
There are two types of cervical cancer:
• Squamous Cell Carcinoma
• Adenocarcinoma
1) Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- This is the most common type of cervical cancer. It is formed from a flat cell covering the outer surface of the cervix.
2) Adenocarcinoma
- This is also a less common type of cervical cancer. It is formed in the glandular cells found in the cervical ducts.
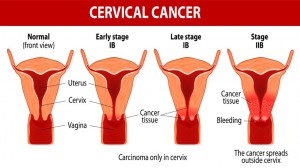
Cervical Cancer Stages
Stage 0 – Cancer is only present in cells on the cervix
Stage 1 – Cancer invades further into the cervix
Stage 2 – Cancer has begun spreading around the cervix
Stage 3 – Cancer has spread to the pelvis
Stage 4 – Cancer has spread to other organs
Cervical Cancer Risk Factors
Risk factors are factors that may increase the risk of a person suffering from cervical cancer. Among them are:
1) Sex activity at a young age
2) Have sex friends
3) Have a sex friend with another sex partner
4) Give birth to many children
5) Human papillomavirus infection (Human Papillomavirus – HPV)
6) Smoking
7) Less maintaining vaginal cleanliness
8) Immunity to protect the body from infectious diseases decreases due to some diseases such as AIDS and others
9) Do not undergo Pap test (‘Pap smear’) periodically
10) From low social class
Cervical Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms / Symptoms are signs that are experienced by someone who signals that the individual is likely to have cervical cancer. Among them are:
1) Pain and bleeding during sex activities
2) Bleeding from abnormal vagina
3) Bleeding from the vagina during the menstrual period
4) Bleeding from the vagina after menopause
5) Pain or swelling in the legs
6) Pain in the back of the lower body
7) Prolonged or excessive fatigue
8) Smelly and abnormal vaginal discharge