Nasopharynx Cancer
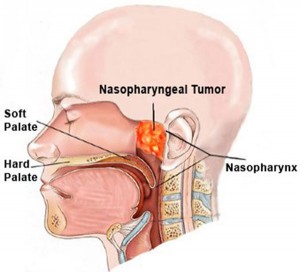
What is Nasopharynx?
- Throat is also named farinks.
- Farinks is divided into 3 parts and nasofarinks are one of them.
- Nasofarinks lies behind the nose and the upper 1/3 of the throat.
- Nasofarinks begin on the back of the nose and leads down to the neck.
- Farinks is a tube length of about 12.7 centimeters (5 inches).
What is Nasopharynx Cancer?
- Cancer that develops in nasopharynx is named nasopharynx cancer.
- It is also named nasopharyngeal carcinoma or NPC (nasopharyngeal carcinoma).
- The Epstein-Barr (EBV) virus also increases the risk of nasopharyngeal cancer.
- Cancer begins when cells in the body divide abnormally and form a tumor.
- Tumors may be benign (non cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Type of Cancer Nasopharynx
Most nasopharyngeal cancers are squamous cell carcinoma – squamous cell carcinomas (flat cells such as skin cells that pass through the inside of the mouth, nose, larynx and throat). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are three nasopharyngeal cancer subtypes:
1) Keratinizing squamous cell cancer – Keratinizing squamous cell cancer (type 1)
2) Non keratinizing squamous cell cancer – Non keratinizing squamous cell cancer (type 2)
3) Carcinoma is different – Undifferentiated carcinomas (type 3)
Nasopharynx Cancer Stage
Stage 0 (Carcinoma In Situ)
Abnormal cells are present in nasopharyngeal linens. This is an early stage of cancer. Some doctors call it pre-cancerous.
Stage I
This stage is the earliest stage of nasopharynx cancer. It may involve all parts of nasopharynx. This cancer may not spread to other parts of the body.
Stage II
At this stage, cancer cells have propagated to the surrounding tissues. There are 2 groups in Phase II.
IIA: cancer occurs in nasopharynx and spread to orofarinks, and / or nasal cavities
IIB: cancer is present in nasopharynx and spread to the lymph nodes in the neck
Stage III
If you are in Level III, it means one of the following:
- Cancer is found in nasopharynx and has spread to lymph nodes about 6 centimeters or less, on both sides of the neck.
- Cancer is found in nasopharynx and has spread into oropharynx and / or nasal cavities and to the lymph nodes about 6 centimeters or less, on both sides of the neck.
- Cancer has spread to nearby bones or sinuses, and may spread to lymph nodes about 6 centimeters or less, on both sides of the neck.
Stage IV
This means that cancer has spread.
IVA: Cancer has spread to skulls, cranium nerves, eyes or hypopharynx. Cancer may also have spread to the lymph nodes about 6 centimeters and slightly less on the neck.
IVB: Cancer has spread to skulls, cranium nerves, eyes or hypopharynx. Cancer may also have spread to the lymph nodes about 6 centimeters and more around the neck.
IVC: cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body such as bones, lungs and brain.
Nasopharynx Cancer Risk Factors
1) Use of tobacco : smoking, and more tobacco use for longer periods, higher risk for cancer
2) Alcohol : Drinking heavily and often alcoholic beverages is a risk factor for head and neck cancer
3) Age : 40 years old or older
4) Decreased immunity : such as AIDS disease increases the risk of getting cancer
5) Diet : Less eating fruits and vegetables
6) Gender : men are twice as likely to risk from women to have NPCs
7) Environment : Excessive exposure to dust and smoke may increase risk factors for NPC.
Nasopharynx Cancer Symptoms
Early symptoms include:
1) The nose is often bloody
2) Hearing problems such as buzzing sounds and pain
3) Nasal congestion
When disease develops, the following conditions may occur:
1) Hearing loss
2) Pain, numb, or paralyzed on the face
3) Coughing blood
4) Swallowing problems
5) It is difficult to breathe or talk that is caused by a sting nose
6) Blurred or shadowed vision
7) Hard to open mouth
Nasopharynx Cancer Prevention
1) Do not use tobacco products.
2) Drink alcohol at a moderate pace.
3) Eat healthy diet. This diet should be rich in cereals, fruits and vegetables.
4) Meet doctors and dentists on a regular basis for cancer screening and screening.